-
SLA
SLA
What is SLA?
In the Amazon ecosystem, SLAs are essential for ensuring consistent performance and reliability across the entire supply chain.
They establish quantitative targets (e.g., shipment times, defect rates, or accuracy thresholds) and outline the penalties or corrective actions if those targets are not met.
SLAs apply across multiple Amazon programmes - including Vendor Central, Seller Central, Direct Fulfilment (DF), and Seller Fulfilled Prime (SFP) - and are a core part of how Amazon enforces operational excellence.
Purpose of an SLA:
- To standardise performance expectations between Amazon and its partners.
- To maintain customer trust by ensuring consistent quality and delivery speed.
- To reduce inefficiencies and disputes through clear accountability.
Common SLA Types in Amazon Operations:
- Fulfilment SLAs:
- Timeframes for processing, packing, and dispatching customer orders.
- Example: “All Prime orders must be shipped within one business day.”
- Delivery SLAs:
- Commitments on end-customer delivery times.
- Example: “99% of SFP orders must arrive within two days.”
- Inbound SLAs:
- Expected timelines for sending shipments to Amazon Fulfilment Centres (FCs).
- Example: “All POs must be delivered within 7 calendar days of ASN confirmation.”
- Customer Service SLAs:
- Response and resolution timeframes for customer inquiries or claims.
- Example: “All customer messages must be answered within 24 hours.”
- Operational Quality SLAs:
- Accuracy metrics for order handling, labelling, and packaging compliance.
- Example: “Perfect Inbound Defect Rate (PIBDR) must remain below 2%.”
Typical SLA Metrics: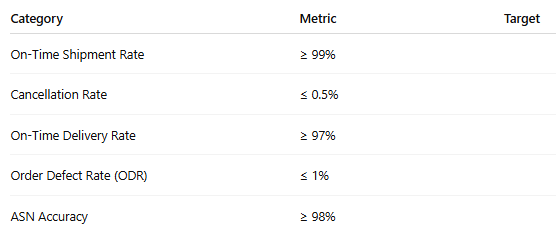 Benefits for Amazon:
Benefits for Amazon:
- Predictability: Ensures fulfilment network stability.
- Customer satisfaction: Guarantees fast, reliable delivery.
- Scalability: Enables consistent performance across thousands of partners.
Benefits for Vendors and Sellers:
- Transparency: Clear expectations and measurable goals.
- Performance insight: Enables tracking and optimisation of operational KPIs.
- Reputation: Consistent SLA compliance can improve buy box eligibility and vendor trust.
Challenges:
- Strict enforcement: Failure to meet SLAs can lead to chargebacks or account suspension.
- Complexity: SLAs vary by region, programme, and category.
- Data dependence: Delays in system updates can trigger false SLA breaches.
Where It’s Applied:
- Vendor Central: Inbound logistics, packaging, and delivery commitments.
- Seller Central: Fulfilment metrics like ODR, Late Shipment Rate, and Pre-Fulfilment Cancellation Rate.
- SFP and DF: Real-time shipment and delivery performance.
- AVS and Operations Teams: Internal SLAs for issue resolution and process turnaround times.
Why It Matters:
SLAs are the backbone of Amazon’s operational reliability.
By enforcing strict performance standards, Amazon ensures that vendors and sellers consistently meet its customer-obsession promise - fast, error-free, and predictable service.
Example:
A Seller Fulfilled Prime (SFP) seller must ship 99% of orders on time and maintain a cancellation rate below 0.5%.
Failure to meet these SLA targets for two consecutive weeks may result in temporary programme suspension.
In short:
SLA (Service Level Agreement) defines the measurable performance standards partners must meet - covering delivery speed, fulfilment accuracy, and operational quality - ensuring Amazon’s high service levels and customer satisfaction are maintained.
Ready to Put Your Knowledge to Use?
Now that you understand the terminology, start using SoldScope to research products, analyze keywords, and grow your Amazon business.
Try for Free